Basics of Machine Learning Series
Notations
- \(m\): Number of training examples
- \(x\)’s: Input variables / features
- \(y\)’s: Output / Target variables
- \((x,y)\): One training example
- \((x^{(i)},y^{(i)})\): \(i^{th}\) training example
Supervised Learning
Formally stated, the aim of the supervised learning algorithm is to use the training Dataset and output a hypothesis function, h where h is a function that takes the input instance and predicts the output based on its learnings from the training dataset.
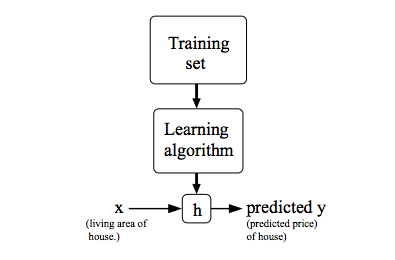
As shown above, say given a dataset where each training instance consists of the area of a house and its price, the job of the learning algorithm would be to come up with a hypothesis, h such that it takes the size of house as input and predicts its price
Hypothesis
Hypothesis is the function that is to be learnt by the learning algorithm by the training progress for making the predictions about the unseen data.
For example, for Linear Regression in One Variable or Univariate Linear Regression, the hypothesis, h is given by
- Where
- \(h_\theta (x)\) is the hypothesis function, also denoted as \(h(x)\) sometimes
- \(x\) is the independent variable
- \(\theta_0\) and \(\theta_1\) are the parameters of the linear regression that need to be learnt